
Introduction
Table of Contents
ToggleAgarwood, derived from the Aquilaria tree, holds a revered place in various cultures due to its unique fragrance and spiritual significance. The global agarwood industry landscape has evolved significantly, reflecting changes in cultivation practices, market demand, and regulatory frameworks. For stakeholders aiming to engage responsibly and profitably.
Oudgo provides insights into navigating this complex market by offering products and expertise that underscore the value of quality and ethical sourcing.
The Agarwood Industry Landscape
Global Production and Cultivation
Natural Formation of Agarwood
Agarwood forms when the Aquilaria tree undergoes a natural defense mechanism, producing resin in response to certain mold infections. This resin-infused wood is what we recognize as agarwood, prized for its aromatic properties.

Cultivation Practices
Traditionally, agarwood was harvested from wild forests, leading to overexploitation. Modern cultivation practices have shifted towards sustainable methods, including plantation-grown agarwood. These practices involve inoculating healthy trees to stimulate resin production, ensuring a more controlled and ethical supply. For detailed insights on how to buy quality agarwood, refer to our comprehensive Guide to Buying Quality Agarwood.

Key Producing Regions
Major agarwood-producing countries include Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Malaysia, and Indonesia. Each region contributes uniquely to the market, offering variations in resin quality and aromatic profiles that influence the global supply and demand dynamics.

Market Demand and Applications
Cultural and Religious Uses
Agarwood’s significance spans across cultures and religions. It is used in various rituals and ceremonies, symbolizing purity and divinity. The cultural importance in regions like the Middle East and Asia drives substantial demand.
Industrial Applications
Beyond traditional uses, agarwood has found its way into industries such as perfumery, where it’s a key ingredient in luxury fragrances. It’s also utilized in traditional medicines and aromatherapy, capitalizing on its supposed therapeutic properties.
Emerging Trends
The market is witnessing agarwood market trends like the development of agarwood-infused products, including cosmetics and wellness items. These innovations are expanding the market, attracting new consumer segments and driving global demand. Understanding market trends highlights the importance of quality evaluation in maintaining the value of agarwood products.
Evaluating Agarwood Quality
Understanding Quality Indicators
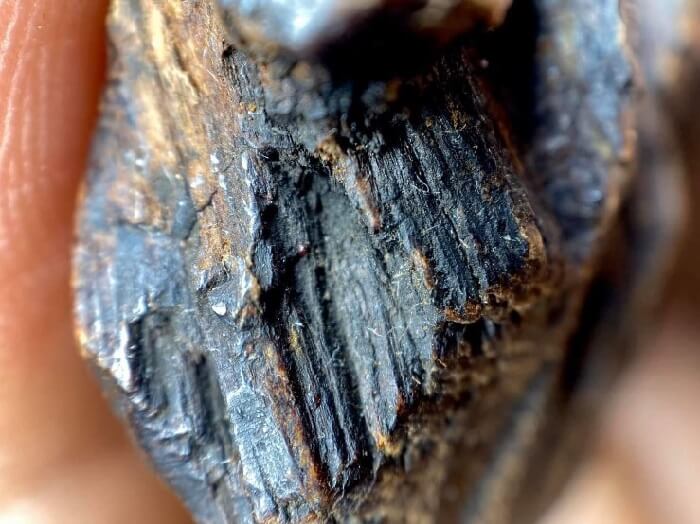
Resin Content and Aroma
The resin content is a primary indicator of agarwood quality. Higher resin levels typically result in a richer, more complex aroma, which is highly valued. The scent profile can range from sweet and floral to deep and woody, influencing its desirability.

Wood Characteristics
Physical properties such as color, density, and texture also play a role in quality assessment. High-quality agarwood is usually darker and denser due to the concentration of resin. Evaluating these wood characteristics requires expertise.

Grading Systems
Various grading systems exist, often region-specific, to categorize agarwood quality. While there’s no universal standard, factors like resin density, scent longevity, and appearance are commonly considered. Understanding these systems is crucial for buyers and sellers.

Challenges in Quality Assessment
Lack of Standardization
The absence of standardized grading leads to inconsistencies, making it challenging to assess quality objectively. This lack of standardization can result in disputes and requires reliance on trusted experts.
Counterfeit Products
The high value of agarwood has led to the proliferation of counterfeit products, including artificially scented wood and synthetic alternatives. These fakes undermine market integrity and pose risks to consumers and investors.


Need for Expert Evaluation
Due to these challenges, the role of specialists in authenticating agarwood is paramount. Experts use their knowledge of resin content assessment and other indicators to verify authenticity, ensuring confidence in transactions.
Economic Factors in the Agarwood Market
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Overharvesting and Scarcity
Historical overharvesting has led to scarcity of wild agarwood, affecting the supply and demand dynamics. This scarcity increases prices and pushes the market towards sustainable sources.
Cultivation Efforts
Cultivation efforts through plantations are mitigating scarcity by providing a steady supply of agarwood. These efforts contribute to market stability and support conservation.
Global Demand Patterns
Demand varies globally, with the Middle East, East Asia, and emerging markets showing significant interest. Understanding these global demand patterns helps in strategizing market approaches.
Market Pricing Mechanisms
Price Determinants
Factors such as quality, origin, and market demand influence the price determinants of agarwood. High-quality, rare agarwood commands premium prices. Analyzing the market dynamics reveals insights into the diverse range of agarwood products available today.
Historical Price Trends
While avoiding previous detailed discussions, it’s notable that prices have generally increased due to scarcity and rising demand. Monitoring these historical price trends is essential for market participants.
Future Projections
Experts predict that demand will continue to grow, potentially driving prices higher. Future projections suggest that sustainable cultivation and technological advancements may balance the market.
Investment Opportunities
Agarwood Plantations
Investing in agarwood plantations offers potential returns due to high market value. However, investors must consider risks like long cultivation periods and market fluctuations.
Commodity Trading
Agarwood is becoming more prominent in commodity trading, attracting investors interested in diversifying portfolios. Knowledge of market dynamics is crucial for success.
Market Entry Strategies
New investors should focus on building relationships, understanding regulatory requirements, and staying informed about market supply and demand dynamics to navigate effectively.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Conservation Efforts
Threats to Wild Populations
Wild Aquilaria trees face threats from illegal logging and habitat loss. These threats to wild populations necessitate conservation efforts to preserve biodiversity.
Sustainable Practices
Implementing sustainable practices, such as regulated harvesting and reforestation, helps protect resources while meeting market demand.
Role of Organizations
Various NGOs and government agencies promote conservation through education, regulation, and support for sustainable initiatives. Their involvement is crucial in shaping the regulatory and ethical considerations of the market.
International Agreements and Compliance
Global Regulations
International agreements, like those from CITES agarwood, impact trade by imposing restrictions to protect endangered species.
Compliance Challenges
Navigating global regulations can be complex due to varying national laws and enforcement levels. Traders must stay informed to ensure compliance and avoid legal repercussions.
Impact on the Industry
Regulations influence supply chains, potentially increasing costs but also promoting sustainability. The industry’s adaptation to these rules shapes its future.
Ethical Sourcing and Fair Trade
Supporting Local Communities
Ethical sourcing involves fair compensation and support for local communities engaged in agarwood production, enhancing their livelihoods.
Consumer Responsibility
Consumers play a role by choosing products from ethical sources, encouraging companies to adopt responsible practices.
Certification Programs
Participation in certification programs ensures transparency and builds trust. Certifications verify that products meet certain ethical and quality standards.
Strategies for Market Participants
Buyers and Collectors
Identifying Quality Sources
Buyers should seek reputable suppliers known for high-quality products and ethical practices. Due diligence is key to identifying quality sources.
Market Research
Staying updated on industry developments helps buyers make informed decisions. Regular market research prevents missteps and uncovers opportunities.
Networking
Building relationships within the industry facilitates access to information and resources, enhancing one’s position in the market.
Producers and Sellers
Enhancing Product Value
Producers can improve product appeal by focusing on quality, authenticity, and unique selling points. Innovations in cultivation and processing contribute to this.
Marketing Approaches
Effective marketing approaches target the right audience, utilizing storytelling about the product’s origin, quality, and ethical aspects.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to regulations is non-negotiable. Producers must ensure compliance to avoid penalties and build a trustworthy reputation.
Investors
Risk Management
Understanding market risks, such as price volatility and regulatory changes, is essential. Diversifying investments and staying informed are prudent strategies.
Diversification
Including agarwood in investment portfolios offers diversification benefits due to its unique market dynamics.
Staying Informed
Continuous learning about technological advancements, market trends, and regulatory shifts is vital for successful investment.
Future Outlook of the Agarwood Market
Technological Advancements
Innovation in Cultivation
Advancements like biotechnology are enhancing cultivation practices, improving yields, and reducing production times.
Quality Testing Technologies
New methods for quality testing, including molecular analysis, are improving authentication and grading accuracy.
Digital Marketplaces
The rise of digital marketplaces is transforming trade, making it easier to connect buyers and sellers globally, and increasing market transparency.
Environmental and Social Impact
Climate Change Effects
Climate change poses challenges such as altered growth conditions and increased pest risks, impacting cultivation.
Community Development
Sustainable practices contribute to community development, offering long-term benefits like employment and education.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Companies are increasingly expected to engage in corporate social responsibility, addressing environmental and social issues as part of their business models.
Global Market Expansion
New Consumer Markets
Emerging economies are showing interest in agarwood, expanding the global market and diversifying demand sources.
Product Diversification
Innovation leads to new agarwood-based products, appealing to broader consumer bases and creating additional revenue streams.
Collaborative Opportunities
Partnerships across industries, such as beauty and wellness sectors, drive growth and open new avenues for the agarwood market.
Conclusion
Navigating the complex agarwood industry landscape requires a comprehensive understanding of its various facets—from production and quality evaluation to economic factors and ethical considerations. By engaging responsibly and staying informed about market supply and demand dynamics, stakeholders can contribute to a sustainable and profitable future for the agarwood market. Embracing innovation, supporting conservation, and fostering collaboration are essential steps towards achieving this goal.
FAQs
1. What is agarwood, and why is it so valuable?
Agarwood is a resinous wood from the Aquilaria tree, known for its unique and rich fragrance. It forms in response to certain fungal infections, causing the tree to produce resin. This rare, aromatic resin is highly valued in perfumery, traditional medicine, and spiritual rituals, making agarwood a luxury commodity with significant cultural and economic importance.
2. How does the global agarwood industry ensure sustainable production?
Sustainable production is achieved through controlled cultivation practices, such as plantation-grown agarwood, which involves inoculating healthy trees to stimulate resin production. These methods reduce reliance on wild trees, helping prevent overexploitation. Conservation efforts and regulated harvesting practices also support sustainable agarwood production.
3. What factors affect the quality and price of agarwood?
Agarwood quality is determined by factors such as resin content, aroma, and physical characteristics like color and density. Higher resin levels and complex scent profiles increase the wood’s value. Regional origin, rarity, and consumer demand also influence pricing, with high-quality, sustainably sourced agarwood commanding premium prices.
4. What are some common uses of agarwood across different industries?
Agarwood is widely used in luxury perfumes, aromatherapy, traditional medicines, and spiritual ceremonies. Recently, agarwood has also found applications in cosmetics, wellness products, and even incense, highlighting its versatility and appeal across different consumer segments.
5. How can consumers ensure they are purchasing authentic agarwood?
Consumers can look for authenticity certificates, reputable sellers, and traceable sourcing information to verify authenticity. Genuine agarwood has a complex, evolving aroma and is usually darker and denser. Seeking expert evaluation and avoiding artificially scented or significantly lower-priced products can also help ensure authenticity.
Author
Pham Thi Mai Huong is the Sales Director of Oudgo, responsible for managing the sales team, developing relationships with customers, and establishing strategic partnerships. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration from Ho Chi Minh City University of Economics and brings over twelve years of experience in sales and market development. Prior to joining Oudgo.Ms. Huong worked with companies specializing in the export and distribution of premium products, where she developed expertise in expanding market reach and driving sales growth. Her leadership and strategic approach have been key in enhancing Oudgo’s sales performance and strengthening its presence in the market see more

