
Introduction
Table of Contents
ToggleAgarwood, often hailed as “liquid gold,” is a rare and precious resinous wood treasured for its captivating fragrance and versatile applications. Derived from the heartwood of Aquilaria trees, this extraordinary material has held a place of admiration across cultures for centuries. This article delves into agarwood’s diverse roles in health, spirituality, and tradition, presenting a fresh perspective on its significance while complementing existing discussions with new insights.
The Essence of Agarwood
Botanical Background
The Aquilaria Tree
The Aquilaria tree belongs to the Thymelaeaceae family and comprises several species native to Southeast Asia, including Aquilaria malaccensis and Aquilaria crassna. These trees thrive in tropical forests across countries like India, Vietnam, and Indonesia. Their geographic distribution is critical to the formation of agarwood, as environmental factors influence resin production.

Formation Process
The natural development of agarwood resin is a fascinating phenomenon. When the Aquilaria tree becomes wounded or infected by certain fungi or bacteria, it produces a dark, aromatic resin as a defense mechanism. This process transforms the otherwise pale, scentless wood into the fragrant and valuable agarwood. Factors contributing to resin production include environmental stressors, microbial invasion, and physical injuries to the tree.
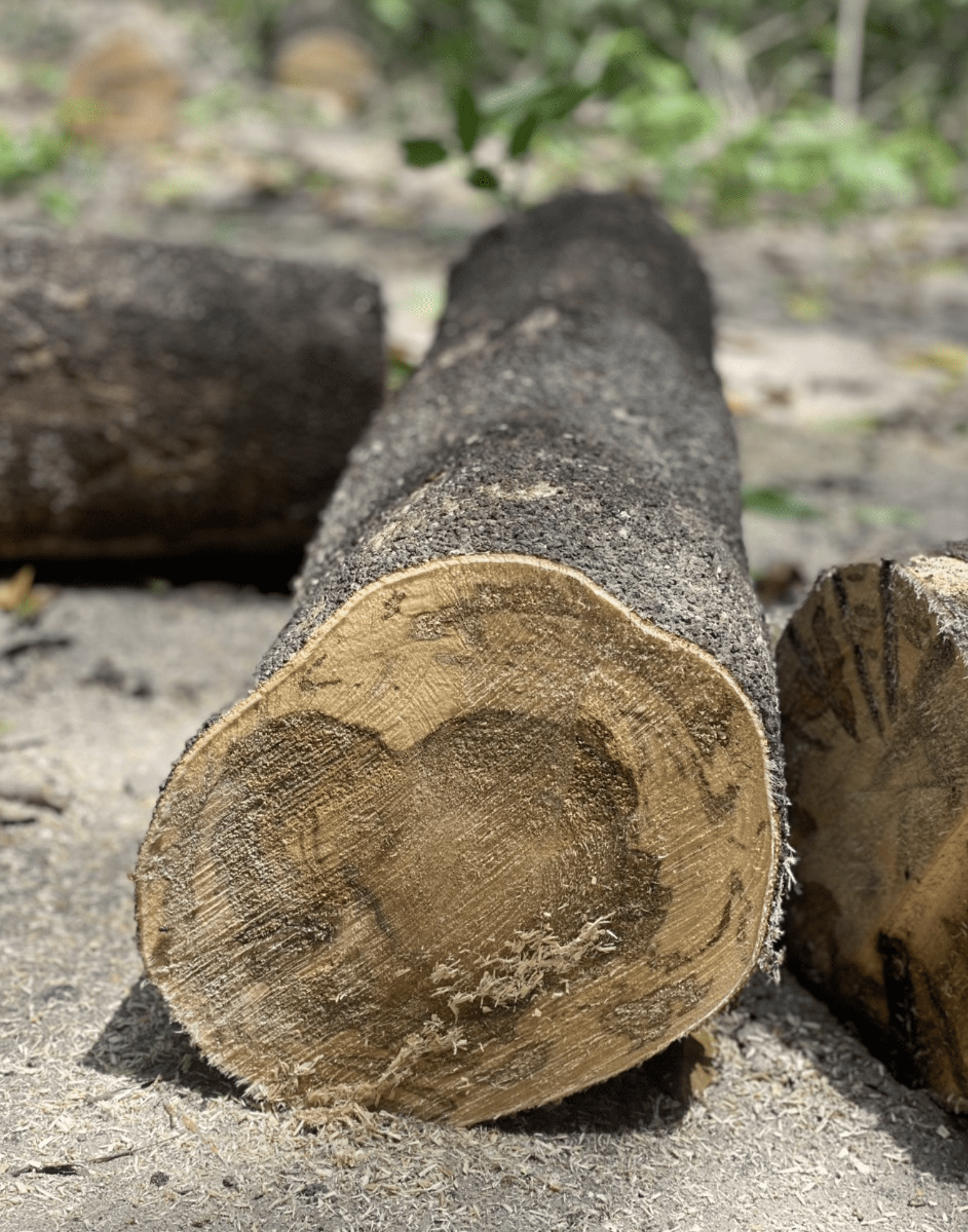

Historical and Cultural Context
Ancient Trade and Use
Historically, agarwood played a significant role in early commerce along the Silk Road and maritime trading routes. Its value made it a highly sought-after commodity in ancient Egypt, China, and the Middle East. The historical significance in various civilizations is evident through its mention in texts like the Sanskrit Vedas and Chinese medicinal manuscripts.

Cultural Symbolism
In many cultures, agarwood represents spiritual purity and is often associated with rituals and ceremonies. Its representation in folklore and traditions highlights its role as a bridge between the physical and spiritual worlds. For instance, in Japanese culture, the art of Kōdō (“Way of Fragrance”) revolves around the appreciation of agarwood scents.

Health Implications of Agarwood
Overview of Therapeutic Properties
General Health Benefits
Agarwood is renowned for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Its resin contains compounds that help reduce inflammation and combat bacterial and fungal infections. Additionally, agarwood has a positive impact on mental well-being, offering calming effects that alleviate stress and anxiety.

Modern Research
Recent studies have begun to validate traditional claims about agarwood’s therapeutic properties. Modern research indicates potential benefits in areas such as neuroprotection, anti-cancer activity, and antimicrobial efficacy. These findings support the continued use of agarwood in contemporary health practices.
Applications in Contemporary Wellness
Aromatherapy and Relaxation
In modern wellness, agarwood is a prized ingredient in aromatherapy. Its rich, woody scent is used in stress-relief practices to promote relaxation and mental clarity. Diffusing agarwood essential oil can create a tranquil environment conducive to meditation and restful sleep.

“Discover how agarwood aromatherapy enhances health and spirit.“
Holistic Health Practices
Agarwood is incorporated into holistic health practices like yoga and meditation. Its aroma enhances focus and deepens the meditative experience, aligning the mind and body. Practitioners believe that agarwood helps in balancing energy and fostering spiritual growth. Understanding the economic implications of agarwood is essential for appreciating its value beyond cultural and health contexts.

Spiritual and Religious Importance
Universal Spiritual Significance
Symbolism in Various Faiths
The spiritual significance of agarwood transcends cultural boundaries. In Buddhism, it symbolizes the transience of life and aids in meditation. In Islam, burning agarwood incense is considered a Sunnah practice, aligning with prophetic traditions. Such symbolism in various faiths underscores common themes of purity, enlightenment, and connection to the divine.

“Learn about the use of agarwood in religion and rituals across cultures.”
Role in Rituals and Ceremonies
Agarwood plays a pivotal role in creating sacred spaces. Its use in rituals and ceremonies involves purifying the environment, invoking spiritual entities, and enhancing the overall spiritual experience. The fragrant smoke of agarwood is believed to carry prayers and intentions to higher realms.
Cultural Expressions
Artistic Inspirations
The allure of agarwood extends into the arts, influencing music, literature, and visual art. Its mention in poetry and stories often symbolizes depth and richness. Such artistic inspirations reflect the profound impact of agarwood on human creativity and expression.
Festivals and Traditions
Participation in cultural celebrations frequently involves agarwood. During festivals like Diwali in India or Ramadan in Islamic countries, burning agarwood enhances the festive atmosphere. Its presence in festivals and traditions signifies joy, purity, and communal harmony.

Traditional Medicinal Uses
Global Traditional Practices
Comparative Overview
Agarwood’s medicinal uses vary across traditional medicine systems. In Ayurveda, it’s used to balance doshas and treat digestive issues. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) employs agarwood to regulate Qi and alleviate pain. Such a comparative overview highlights its versatility and widespread acceptance. “Explore more about the health benefits of agarwood in traditional medicine.“
Common Remedies
Common remedies involving agarwood address ailments like asthma, rheumatism, and gastrointestinal disorders. Its application can be through ingestion, topical treatments, or inhalation, depending on the ailment and tradition.

Transition to Modern Medicine
Integration into Current Therapies
Today, agarwood is found in herbal supplements and alternative medicine. Its integration into current therapies offers a bridge between ancient wisdom and modern science, providing holistic options for health and wellness.
Scientific Exploration
Ongoing scientific exploration aims to isolate active compounds in agarwood for pharmaceutical use. Research into its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties holds promise for new medicinal applications.
Sustainability and Conservation Efforts
Environmental Concerns
Threats to Aquilaria Trees
Overharvesting and habitat loss pose significant threats to Aquilaria trees. The high demand for agarwood has led to unsustainable practices that endanger the species and disrupt ecosystems.
Illegal Trade Issues
The illegal trade of agarwood exacerbates environmental concerns. Poaching and unregulated harvesting contribute to the decline of wild Aquilaria populations, undermining conservation efforts.
Conservation Initiatives
Sustainable Harvesting
Efforts towards sustainable harvesting include cultivating Aquilaria trees in plantations and implementing inoculation techniques to produce resin without harming the trees. Such cultivation and plantation efforts aim to meet demand while preserving wild populations. Addressing the ecological impact of agarwood harvesting is vital to ensure that the traditional uses of agarwood can continue sustainably.
Regulatory Measures
International agreements like the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) regulate the trade of agarwood. These regulatory measures protect the species by ensuring that trade is legal and sustainable.

Ethical Sourcing and Consumer Responsibility
Importance of Ethical Practices
Supporting Indigenous Communities
Ethical sourcing supports indigenous communities who rely on agarwood for their livelihoods. Fair trade practices ensure economic benefits and promote sustainable harvesting methods.
Ensuring Product Authenticity
Purchasing authentic agarwood products helps avoid counterfeit items that may not offer the same health benefits or quality. Ensuring product authenticity also supports legitimate producers and conservation efforts.

Consumer Guidelines
Making Informed Purchases
Consumers can identify reputable sources by researching brands, seeking certifications, and understanding the origin of the agarwood. Making informed purchases contributes to ethical trade practices.
Contributing to Sustainability
By supporting conservation-friendly products and companies committed to sustainable practices, consumers play a role in preserving agarwood for future generations. Contributing to sustainability ensures that the multifaceted significance of agarwood endures.
Conclusion
Recap of Agarwood’s Multifaceted Role
Agarwood holds a unique place at the intersection of health, spirituality, and tradition. Its therapeutic properties offer numerous health benefits, while its spiritual significance enriches religious and cultural practices. The traditional uses of agarwood continue to influence modern wellness and holistic health approaches.
Future Outlook
The emphasis on sustainability is crucial for the future of agarwood. Conservation efforts and responsible consumption are necessary to protect this valuable resource. With continued scientific exploration and ethical practices, agarwood can remain a cherished element of global heritage.
Final Thoughts
Embracing the rich legacy of agarwood involves appreciating its diverse roles and acknowledging the responsibility to preserve it. By supporting sustainable practices and understanding its significance, we can ensure that agarwood continues to inspire and benefit humanity.
By understanding the multifaceted significance of agarwood, we not only honor its historical and cultural legacy but also contribute to its sustainable future. Whether through appreciating its health benefits, participating in its spiritual practices, or advocating for ethical sourcing, our actions can preserve the essence of agarwood for generations to come.
FAQs
1. What makes agarwood so valuable and unique?
Agarwood is valued for its rare, rich fragrance and spiritual significance. It forms only when Aquilaria trees produce resin in response to fungal infection or injury, creating a unique aromatic wood. Its rarity, complex aroma, and deep-rooted cultural importance contribute to its high demand and value in the global market.
2. How is agarwood used in health and wellness?
Agarwood is used in aromatherapy for its calming effects, helping to relieve stress and promote mental clarity. Traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) utilize agarwood for ailments such as digestive issues, asthma, and pain relief. Its therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects, make it a popular choice in modern holistic health practices.
3. What is the spiritual significance of agarwood in different cultures?
Agarwood holds spiritual importance across various cultures and religions. In Buddhism, it symbolizes impermanence and aids meditation, while in Islam, it’s used in purification rituals and is mentioned in prophetic traditions. Its use in religious rituals creates sacred spaces, believed to purify environments and connect to the divine.
4. How can consumers ensure they’re purchasing ethically sourced agarwood?
To support ethical sourcing, consumers should look for products with certifications like CITES, indicating compliance with sustainability standards. Researching brands, verifying authenticity, and choosing fair trade products from reputable sellers help ensure the agarwood is sourced responsibly, benefiting both the environment and local communities.
5. What conservation efforts are in place to protect agarwood?
Conservation efforts include cultivating Aquilaria trees on plantations, using inoculation techniques to produce resin sustainably, and adhering to CITES regulations that restrict illegal trade. These initiatives aim to preserve wild populations, ensuring agarwood’s availability for future generations while supporting the ecosystems and communities that rely on it.
Author
Pham Thi Mai Huong is the Sales Director of Oudgo, responsible for managing the sales team, developing relationships with customers, and establishing strategic partnerships. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration from Ho Chi Minh City University of Economics and brings over twelve years of experience in sales and market development. Prior to joining Oudgo.Ms. Huong worked with companies specializing in the export and distribution of premium products, where she developed expertise in expanding market reach and driving sales growth. Her leadership and strategic approach have been key in enhancing Oudgo’s sales performance and strengthening its presence in the market see more
