
Introduction
Table of Contents
ToggleAgarwood, a highly valued fragrant wood, plays a significant role in global trade due to its use in perfumery, traditional medicine, and religious rituals. The soaring demand has led to overexploitation, resulting in illegal activities that threaten the species’ survival. Understanding the legal issues of agarwood trade and adhering to agarwood industry landscape are crucial for ensuring sustainability and legality in the industry.

Overview of Agarwood Trade
What is Agarwood?
Agarwood is a dark, resinous heartwood formed in Aquilaria trees when they become infected with a specific type of mold. This precious material is prized for its unique aroma and is used extensively in incense, perfumes, and traditional healing practices. The economic importance of agarwood has made it a lucrative commodity in the international market. Understanding what agarwood is helps to grasp the importance of legal protections for this valuable resource.

Global Demand and Supply
Major agarwood-producing countries include Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Malaysia, and Indonesia. The international trade of agarwood is driven by high demand from regions like the Middle East, East Asia, and parts of Europe. This demand has led to unsustainable harvesting practices, severely impacting wild populations and ecosystems.

Legal Framework Governing Agarwood
International Trade of Agarwood
The international trade of agarwood involves complex regulations to prevent overexploitation. Cross-border trade poses challenges due to varying laws and enforcement levels in different countries. Traders must navigate these complexities to operate legally.
CITES and Agarwood
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES agarwood regulations) plays a pivotal role in controlling agarwood trade. Several Aquilaria species are listed under CITES Appendix II, which means their trade is allowed but strictly regulated. Compliance requires obtaining CITES permits and proper documentation to ensure that the trade does not threaten the species’ survival.
National Regulations
Each agarwood-producing country has its own set of regulations governing the harvesting, processing, and export of agarwood. For instance, countries may require harvesting permits, impose quotas, or completely ban the harvesting of wild agarwood. Penalties for non-compliance can include fines, imprisonment, and confiscation of goods. Additionally, the cultural significance of agarwood underscores the need for a legal framework to protect it.

Legal Issues in Agarwood Trade
Illegal Harvesting and Poaching
Illegal harvesting remains one of the most pressing legal issues of agarwood trade. Poachers often target protected areas, decimating wild populations of Aquilaria trees. This not only threatens biodiversity but also undermines legal and sustainable trade efforts.
Smuggling and Black Markets
Smuggling is rampant due to the high agarwood export regulations that restrict supply. Illegally obtained agarwood is funneled through black markets, using sophisticated networks to evade law enforcement. This illicit trade has significant economic and social implications, including loss of revenue for governments and funding of other illegal activities.
Mislabeling and Fraud
The mislabeling of agarwood products presents a significant legal challenge, as dishonest traders often pass off inferior or synthetic goods as genuine agarwood, misleading consumers and violating consumer protection laws. This type of fraud not only erodes market trust but also invites legal repercussions. Establishing strong legal frameworks is essential for differentiating real and fake agarwood, safeguarding consumers from deception and maintaining the integrity of the market.
Consumers play a role by choosing products from ethical sources, encouraging companies to adopt responsible practices. Additionally, understanding the guide to buying quality agarwood can help consumers make informed ethical choices.
Intellectual Property Rights
Disputes over patents and trademarks related to agarwood products have emerged, raising legal issues concerning intellectual property rights. Additionally, there are concerns about biopiracy, where traditional knowledge and resources are exploited without proper compensation to indigenous communities.

Agarwood Export Regulations
Export Procedures and Requirements
Compliance with agarwood export regulations is essential for legal trade. Exporters must obtain necessary documentation, including CITES export permits, which certify that the agarwood was harvested sustainably and legally. Failure to secure proper permits can result in shipment seizures and legal penalties.
Compliance with Importing Countries’ Laws
Exporters must also adhere to the laws of the destination country. Understanding and complying with importing countries’ regulations is vital to avoid legal complications. Aligning with international standards fosters trust and facilitates smoother trade relations.
Case Studies of Regulatory Compliance
Successful compliance examples demonstrate the benefits of adhering to agarwood regulations. Companies that follow legal protocols enjoy access to international markets, build reputable brands, and contribute to sustainable industry practices. Conversely, enforcement actions against violators serve as warnings about the consequences of non-compliance.
Challenges in Enforcing Agarwood Regulations
Limited Resources and Enforcement Capacity
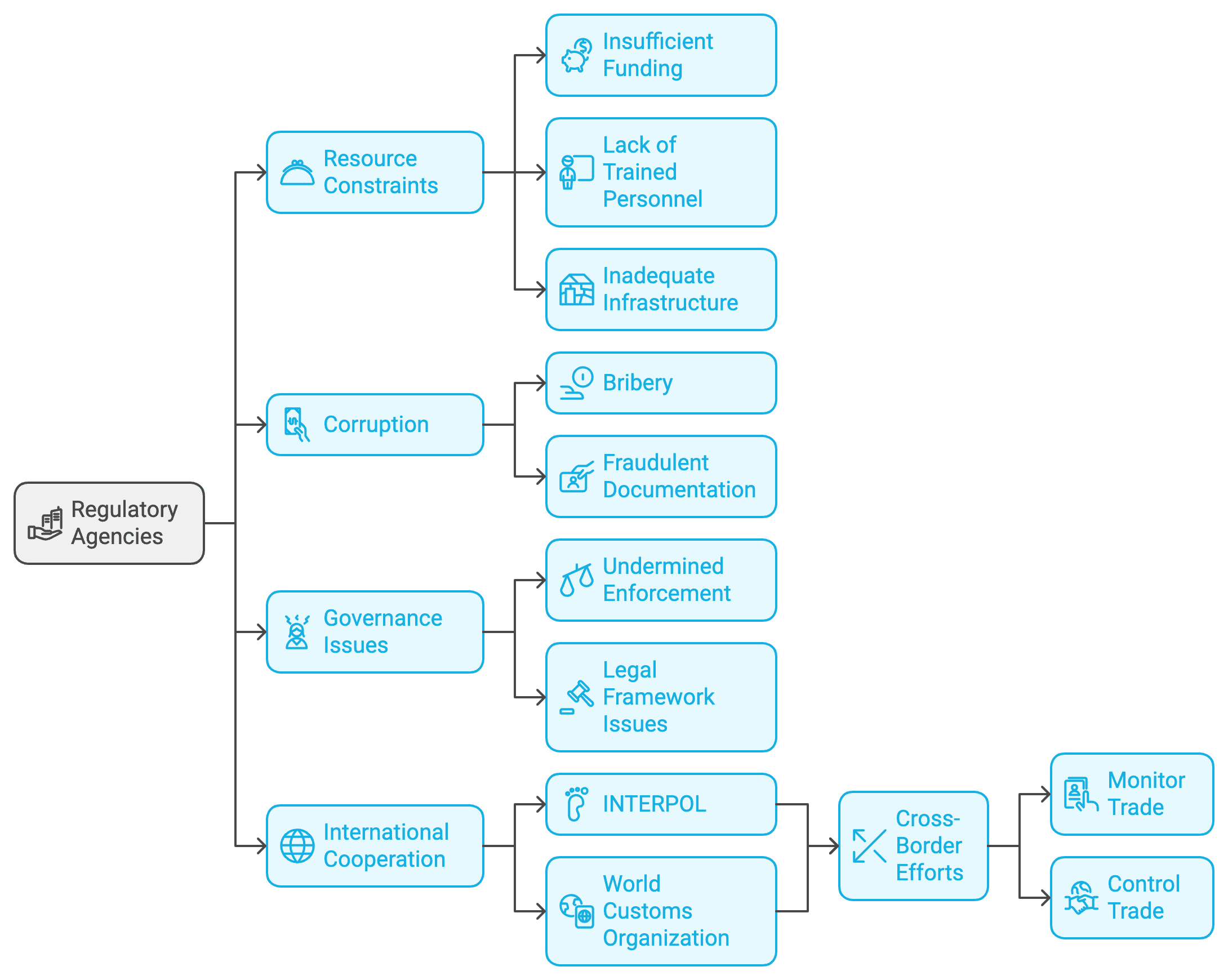
Regulatory agencies often face resource constraints, limiting their ability to enforce agarwood regulations effectively. Insufficient funding, lack of trained personnel, and inadequate infrastructure hinder enforcement efforts, allowing illegal activities to persist.
Corruption and Governance Issues
Corruption can undermine enforcement by facilitating illegal trade through bribery and fraudulent documentation. Addressing governance issues is crucial for the integrity of agarwood export regulations and the overall legal framework.
International Cooperation
International collaboration is essential to combat the illegal international trade of agarwood. Organizations like INTERPOL and the World Customs Organization support cross-border efforts to monitor and control trade. Sharing intelligence and best practices enhances enforcement capabilities globally. Keeping abreast of agarwood market trends is essential for regulatory bodies to adapt laws that protect this valuable resource.
Sustainable and Legal Trade Practices
Cultivation and Plantation Initiatives
Promoting sustainable agarwood production through cultivation and plantation initiatives addresses the supply-demand imbalance. Plantation-grown agarwood reduces pressure on wild populations and provides a legal source for the market. This approach aligns with agarwood regulations and supports conservation goals.
Certification and Traceability
Implementing certification schemes ensures that agarwood products are sourced legally and sustainably. Technologies like blockchain and DNA testing enhance traceability, allowing consumers and authorities to verify the origin of products. Certification builds consumer confidence and supports compliance with CITES agarwood regulations. The health benefits of agarwood further necessitate the establishment of regulations to ensure its safe usage and authenticity.
Community Involvement and Livelihoods
Engaging local communities in sustainable harvesting practices provides alternative income sources and reduces reliance on illegal activities. Community-based management fosters stewardship of resources and contributes to the enforcement of agarwood regulations at the grassroots level.

Future of Agarwood Trade Regulations
Evolving Legal Frameworks
As awareness of the legal issues of agarwood trade grows, legal frameworks are evolving. Stricter laws and enhanced enforcement mechanisms are anticipated, which may impact industry operations. Staying informed about regulatory changes is crucial for traders and stakeholders.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology offer new tools for enforcing agarwood regulations. DNA barcoding can authenticate species, while blockchain provides transparent supply chain records. These innovations have the potential to improve compliance and deter illegal activities significantly. Regulations influence supply chains, potentially increasing costs but also promoting sustainability. For a deeper insight into how these factors affect agarwood price and influencing factors, refer to our dedicated section.
Balancing Conservation and Commerce
Achieving a balance between conservation and commercial interests is essential for the sustainable future of the agarwood industry. Policymakers, businesses, and communities must collaborate to develop strategies that protect resources while supporting economic development. This balance is key to resolving the legal issues of agarwood trade.

Conclusion
Adhering to agarwood export regulations and addressing the legal issues of agarwood trade are imperative for the sustainability and legality of the industry. Stakeholders must commit to ethical practices, comply with CITES agarwood requirements, and support initiatives that promote conservation. By collectively taking responsibility, we can ensure that the international trade of agarwood thrives without compromising the species and ecosystems upon which it depends.
FAQs
1. What is agarwood, and why is it regulated in international trade?
Agarwood is a resinous wood from Aquilaria trees, valued for its fragrance and used in perfumery, traditional medicine, and religious rituals. Due to its high demand, overharvesting has endangered wild populations, leading to regulations by organizations like CITES to ensure sustainable and legal trade, protecting both the species and its habitat.
2. How does CITES impact the agarwood trade?
CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) regulates the international trade of agarwood by requiring permits to ensure that trade does not threaten the species’ survival. Listed under CITES Appendix II, certain Aquilaria species can be traded legally with proper documentation, helping to prevent illegal and unsustainable harvesting.
3. What are the legal challenges in agarwood trade?
The agarwood trade faces several legal challenges, including illegal harvesting, smuggling, and counterfeit products. Mislabeling and intellectual property issues, such as biopiracy, also complicate trade, as some regions exploit traditional knowledge without compensation to indigenous communities. Compliance with international and local regulations is essential to address these challenges.
4. How can consumers verify the authenticity of agarwood products?
Consumers can look for certification and traceability systems that confirm the legal and sustainable sourcing of agarwood. Reputable sellers provide CITES permits and authenticity certificates, and some companies use technologies like DNA testing or blockchain to verify the origin of their products, ensuring consumers receive genuine agarwood.
5. What role does technology play in supporting sustainable agarwood trade?
Technological advancements such as DNA barcoding and blockchain enhance traceability and authentication in the agarwood trade. These technologies make it easier to verify species origin and track products through the supply chain, supporting compliance with regulations and deterring illegal activities, while promoting sustainable practices in the industry.
Author
Pham Thi Mai Huong is the Sales Director of Oudgo, responsible for managing the sales team, developing relationships with customers, and establishing strategic partnerships. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration from Ho Chi Minh City University of Economics and brings over twelve years of experience in sales and market development. Prior to joining Oudgo.Ms. Huong worked with companies specializing in the export and distribution of premium products, where she developed expertise in expanding market reach and driving sales growth. Her leadership and strategic approach have been key in enhancing Oudgo’s sales performance and strengthening its presence in the market see more
