
Agarwood, one of nature’s most valuable resins, faces significant challenges due to its high demand and overharvesting. Implementing sustainable cultivation and harvesting practices is essential to preserve this precious resource while supporting the economic benefits it provides. This article explores the importance of sustainability in agarwood production, outlines effective cultivation and harvesting methods, discusses the challenges faced, and highlights successful case studies that demonstrate the viability of sustainable practices.
Table of Contents
Toggle
I. Introduction
With the global demand for agarwood surging, the need for sustainable cultivation and harvesting practices has never been more critical. Agarwood plantations not only provide a steady supply of fragrant resin but also play a pivotal role in conservation efforts and maintaining ecological sustainability. This article delves into the significance of sustainable practices in agarwood production, outlining methods that balance economic viability with environmental responsibility.
II. Importance of Sustainable Cultivation and Harvesting
A. Environmental Impact
The unsustainable harvesting of agarwood trees leads to deforestation and habitat loss, disrupting forest ecosystems and reducing biodiversity. Overexploitation can result in the decline of Aquilaria species, making agarwood an endangered resource.
- Deforestation and Habitat Loss: Overharvesting for agarwood disrupts natural habitats, threatening countless wildlife species and diminishing forest health.
- Soil and Water Conservation: Sustainable practices help maintain soil fertility and water quality, essential for the longevity of agarwood plantations and surrounding ecosystems.

B. Economic Benefits
Adopting sustainable practices ensures the long-term viability of agarwood production, providing continuous economic benefits without depleting natural resources.
- Long-Term Viability: Sustainable cultivation secures a steady supply of agarwood, supporting the fragrance industry and traditional medicine markets.
- Market Stability: By preventing overharvesting, sustainable practices help maintain market stability, ensuring fair prices and reliable supply chains for producers and consumers alike.

C. Social Responsibility
Sustainable agarwood production fosters community involvement and promotes ethical practices, ensuring that local communities benefit from agarwood harvesting without compromising their environment.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in sustainable practices empowers them, providing economic opportunities while preserving their natural surroundings.
- Ethical Practices: Implementing fair trade and ethical harvesting ensures that agarwood production respects traditional knowledge and provides equitable benefits to all stakeholders.

III. Sustainable Cultivation Methods
A. Plantation Cultivation
Plantation cultivation is a cornerstone of sustainable agarwood production, providing a controlled environment for Agararia species to thrive and produce resin.
- Establishment of Plantations: Selecting suitable sites with optimal soil conditions and climate is crucial for successful agarwood plantations. Proper site preparation ensures healthy tree growth and resin production.
- Tree Selection and Propagation: Choosing the right Aquilaria species, such as Aquilaria malaccensis and Aquilaria sinensis, and utilizing propagation techniques like grafting and seeding enhances resin yield and quality.

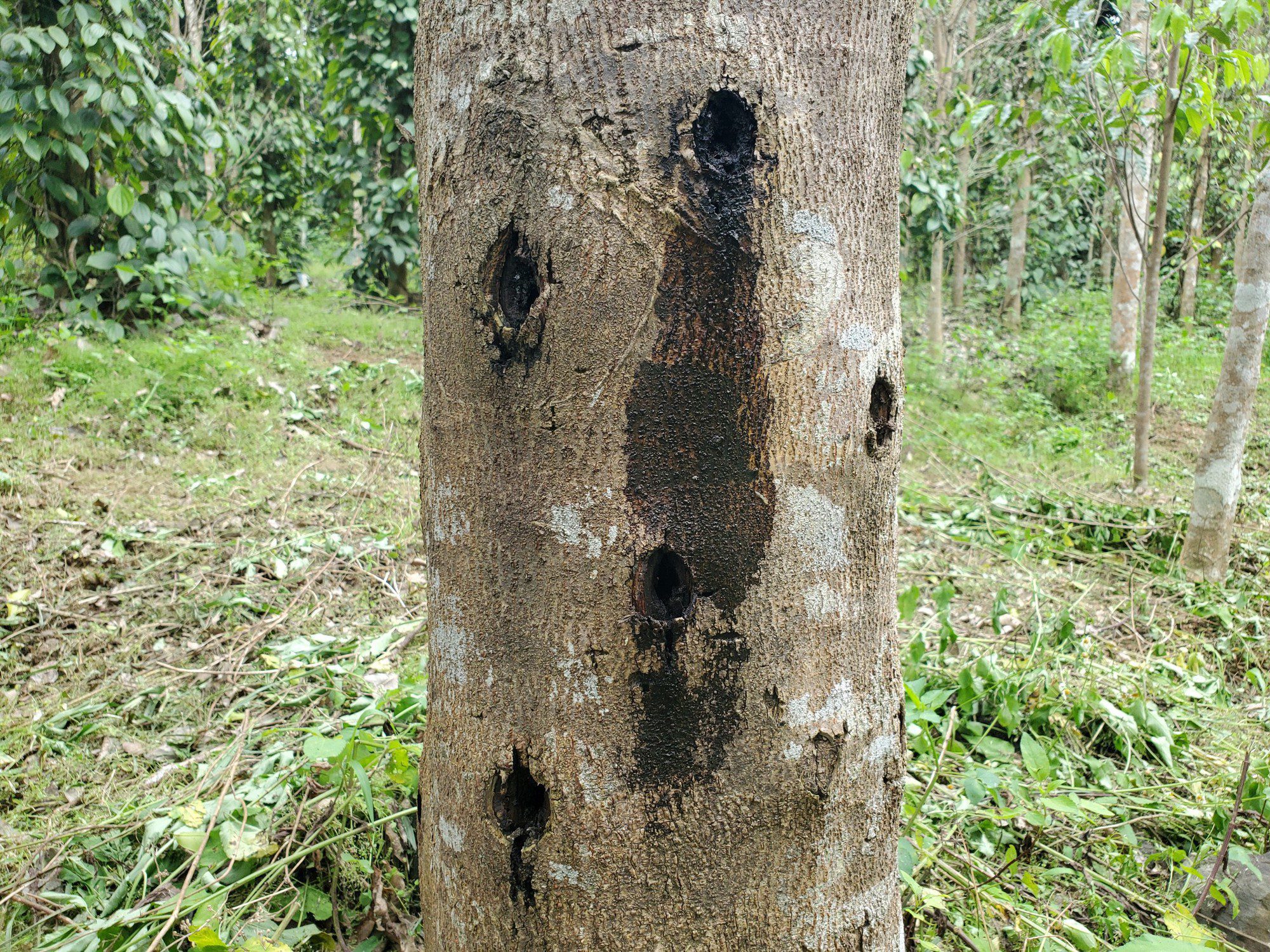
B. Artificial Inoculation
Artificial inoculation techniques are employed to stimulate resin production in agarwood trees, mimicking natural stressors and infections.
- Inoculation Techniques: Methods such as mechanical wounding and introducing Phialophora parasitica fungus induce resin production, accelerating the agarwood formation process. These techniques take into account the biological characteristics of agarwood trees, ensuring that the methods used are compatible with the natural processes of resin formation. Controlled environments allow for predictable and efficient resin production, increasing yield while preserving the health of the trees.
- Controlled Environment: Artificial inoculation allows for predictable and efficient resin production, increasing resin yield and reducing the time required for agarwood formation.

C. Organic Farming Practices
Implementing organic farming practices ensures that agarwood cultivation is environmentally friendly and sustainable.
- Natural Fertilization and Pest Control: Utilizing organic fertilizers and natural pest control methods maintains tree health without relying on harmful chemicals, promoting eco-friendly practices.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Efficient use of resources like water and soil supports the growth of healthy agarwood plantations, ensuring long-term resource sustainability.
IV. Sustainable Harvesting Techniques
A. Controlled Harvesting
Controlled harvesting methods are essential to ensure that agarwood trees can recover and continue producing resin sustainably.
- Harvesting Cycles: Implementing regular harvesting cycles allows trees time to regenerate, ensuring continuous resin production without overexploitation.
- Selective Logging: Using selective logging techniques minimizes damage to agarwood trees and their surroundings, preserving forest integrity and promoting sustainable extraction.

B. Certification and Standards
Adhering to international certification standards like CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) regulates agarwood trade and ensures that harvesting practices meet sustainability criteria.
- International Certifications: Obtaining certifications helps authenticate sustainable agarwood products, building trust with consumers and facilitating ethical trade.
- Adherence to Standards: Ensuring that plantations and harvesting practices comply with international sustainability standards promotes responsible agarwood production and trade.
C. Technology and Innovation
Leveraging technology and innovation enhances the efficiency and sustainability of agarwood cultivation and harvesting.
- Monitoring and Management Tools: Utilizing GIS mapping and remote sensing technologies allows for effective monitoring of plantation health and harvesting activities, ensuring sustainable practices are maintained.
- Innovative Techniques: Adopting new technologies such as digital monitoring systems and automated harvesting tools improves efficiency and reduces the environmental impact of agarwood production.

V. Challenges and Solutions in Sustainable Practices
A. Environmental Challenges
Climate change and pest management pose significant challenges to sustainable agarwood cultivation.
- Climate Change: Altered weather patterns affect agarwood tree growth and resin production. Implementing climate-resilient practices helps mitigate these impacts.
- Pest and Disease Management: Addressing pests and diseases through integrated pest management (IPM) techniques ensures healthy plantations and sustained resin production.
B. Economic and Logistical Challenges
High initial costs and market fluctuations can hinder the adoption of sustainable practices.
- High Initial Costs: Investing in sustainable plantations and advanced harvesting technologies requires significant upfront capital. Financial incentives and government support can alleviate these barriers.
- Market Fluctuations: Stabilizing the agarwood market through long-term contracts and fair pricing strategies ensures economic sustainability for farmers and businesses.
C. Social and Cultural Challenges
Engaging local communities and providing adequate education and training are essential for the successful implementation of sustainable practices.
- Local Community Engagement: Involving local communities in sustainable cultivation and harvesting promotes shared benefits and community empowerment.
- Education and Training: Providing training on sustainable methods and ethical practices equips farmers and plantation managers with the knowledge needed to maintain sustainability.
VI. Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Practices
A. Successful Plantation Models
Case Study 1: Malaysia’s Sustainable Agarwood Plantations
Malaysia has established successful sustainable agarwood plantations by integrating artificial inoculation techniques and adhering to international certification standards. These plantations have achieved high resin yields while maintaining ecological balance and supporting the local economy.

Case Study 2: Vietnam’s Innovative Inoculation Projects
Vietnam has pioneered innovative artificial inoculation projects that use Phialophora parasitica to enhance resin production. These projects demonstrate how technology and innovation can drive sustainable practices and increase resin yield without harming natural forests.

B. Community-Led Initiatives
Case Study 1: Indonesia’s Community-Managed Farms
In Indonesia, community-managed agarwood farms have successfully implemented sustainable harvesting techniques. These initiatives involve local communities in decision-making processes, ensuring ethical practices and fair trade while promoting biodiversity preservation.
Case Study 2: Thailand’s Collaborative Efforts
Thailand’s collaborative efforts between governments and local communities have led to the development of sustainable agarwood plantations. These partnerships focus on capacity building and knowledge sharing, enhancing the economic benefits and environmental sustainability of agarwood production.
VII. Future of Sustainable Agarwood Cultivation and Harvesting
A. Emerging Trends
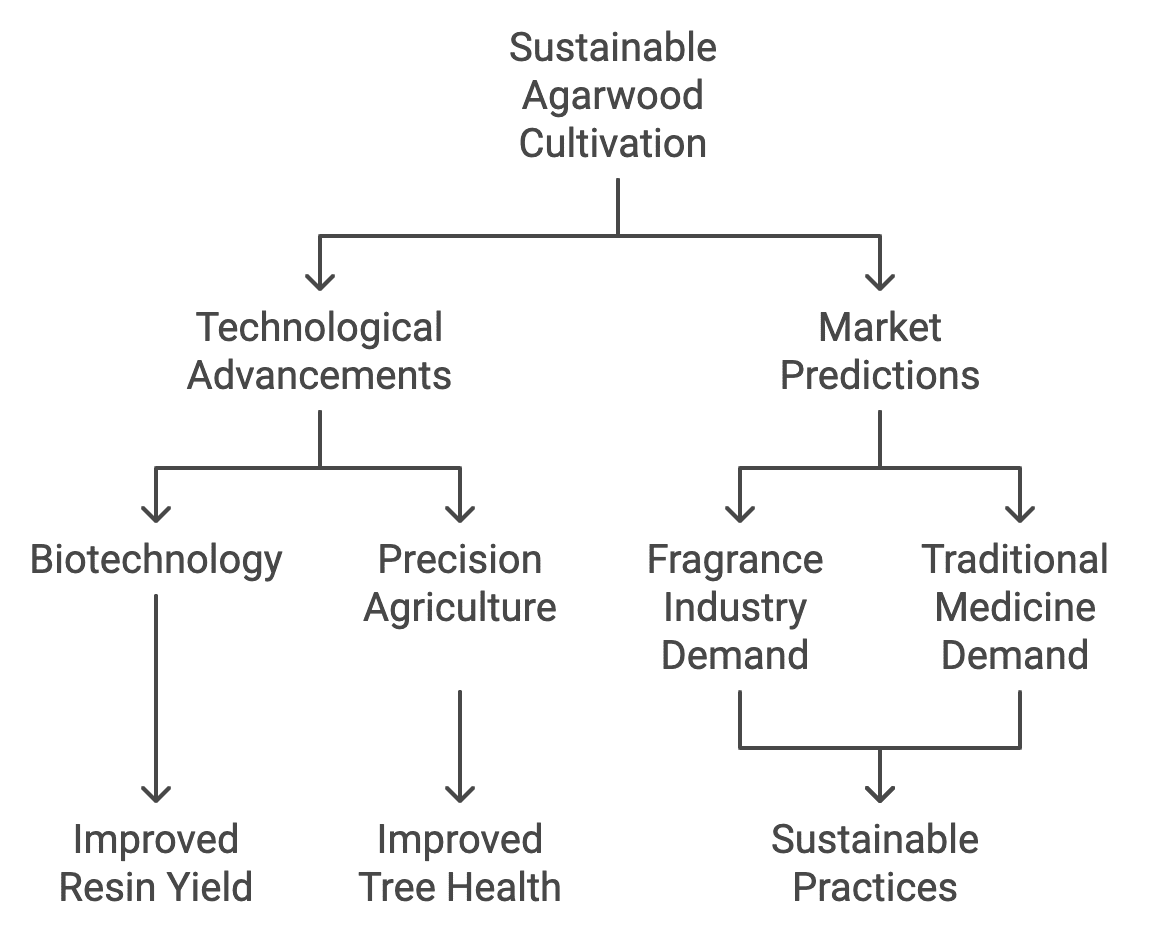
The future of sustainable agarwood cultivation is shaped by technological advancements and evolving market demands.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations such as biotechnology and precision agriculture are set to revolutionize agarwood cultivation, improving resin yield and tree health.
- Market Predictions: The agarwood market is expected to grow, driven by increasing demand in the fragrance industry and traditional medicine sectors. Sustainable practices will be crucial in meeting this demand responsibly.
B. Policy and Regulation Developments
Upcoming regulations and government incentives will play a significant role in promoting sustainable agarwood practices.
- Upcoming Regulations: Stricter regulations on agarwood trade and harvesting practices will ensure compliance with sustainability standards.
- Incentives for Sustainability: Governments and NGOs are providing incentives to encourage sustainable cultivation and ethical harvesting, supporting conservation efforts and economic sustainability.
C. Collaborative Efforts and Global Partnerships
International collaboration and global partnerships are
essential for advancing sustainable agarwood practices worldwide.
- International Collaboration: Partnerships between countries, research institutions, and organizations facilitate the exchange of best practices and technological innovations, enhancing the overall sustainability of agarwood production.
- Knowledge Sharing: Global platforms and conferences promote knowledge sharing and capacity building, enabling countries to implement effective sustainable practices and conservation strategies.

VIII. Conclusion
The sustainable cultivation and harvesting of agarwood are imperative for preserving this precious natural resource while supporting the economic benefits it offers. By adopting sustainable practices, investing in innovative techniques, and fostering community involvement, the agarwood industry can thrive without compromising environmental integrity.
Preserving agarwood requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, and local communities to implement and maintain sustainable cultivation and harvesting methods. As we move forward, embracing technological advancements and fostering global partnerships will be key to ensuring the future sustainability of agarwood, allowing this remarkable resin to continue enriching our lives for generations to come.
FAQs
1. Why is sustainable cultivation and harvesting of agarwood important?
Sustainable practices are crucial to prevent overharvesting, protect natural habitats, and ensure the long-term availability of agarwood. These methods also support biodiversity, economic stability, and ethical resource management.
2. What are the key methods for sustainable agarwood cultivation?
Key methods include plantation cultivation, artificial inoculation to stimulate resin production, and the adoption of organic farming practices. These techniques help balance resin yield with environmental conservation.
3. What challenges does the agarwood industry face in adopting sustainable practices?
The industry faces challenges like high initial costs, climate change impacts, market fluctuations, and the need for community education and engagement. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration, innovation, and government support.
4. How does sustainable agarwood production benefit local communities?
Sustainable production provides economic opportunities for local communities, fosters ethical harvesting practices, and ensures their involvement in preserving natural resources, creating a balance between livelihood and environmental conservation.
5. What role does technology play in sustainable agarwood practices?
Technology plays a critical role by enabling precise monitoring through GIS mapping, enhancing resin production with advanced inoculation techniques, and improving efficiency in cultivation and harvesting processes. These innovations make sustainable practices more effective and scalable.
Author
Tran Thi Bich Ngoc is the Head of Production at Oudgo, overseeing the entire production process from agarwood harvesting to processing and packaging the final products. She holds a Bachelor’s degree in Biotechnology from Hanoi University of Science and Technology and brings over fifteen years of experience in the agarwood production industry. Prior to joining Oudgo.Ms. Ngoc worked with companies specializing in the production of natural cosmetics and health care products. Her extensive expertise ensures the highest quality and efficiency in Oudgo’s production operations, contributing significantly to the company’s reputation for excellence see more
